Ziraat Bank continues to support investment projects that will protect the environment and reduce the negative effects of climate change. Accordingly, the Bank has established an Environmental and Social Impact Management Policy with the aim of integrating the universally accepted principles of sustainability into its business model. With this policy, which determines the environmental and social impact management principles, Ziraat Bank prioritizes that the projects it finances include a high environmental and social contribution.
EVERY YEAR, ZIRAAT BANK INCREASES ITS CONTRIBUTION TO FIGHTING THE CLIMATE CRISIS AND GLOBAL WARMING. THE BANK WORKS WITH AN INSTITUTIONAL APPROACH BASED ON PROVIDING OPTIMAL EFFICIENCY IN THE USE OF RESOURCES AND REDUCING WASTE.

GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS
Ziraat Bank completed its greenhouse gas inventory studies by collecting energy consumption data/statements of domestic branches, Head Office and money group centers for 2022.
In the Bank’s sustainability reporting, electricity consumption in the years before 2017 was calculated by considering the average prices over the invoices, while calculations were made by considering the actual consumption in 2017 and the average prices after 2018. The theoretical payment amounts and the unit electricity price of the relevant year are taken into account in the calculation of emissions from electricity consumption in 2022.
For the scope of greenhouse gas emissions, the considerations described in Scope 1 and Scope 2 of the GHG Protocol were used. In 2022, IPCC and Defra references and TIER-1 Methodology were applied for greenhouse gas calculations within the determined limits, and TIER-2 Methodology was applied for activity data with national data (electricity). The IPCC AR5 evaluation report was used for the KIP (Global Warming Potential) coefficients used in the calculations.
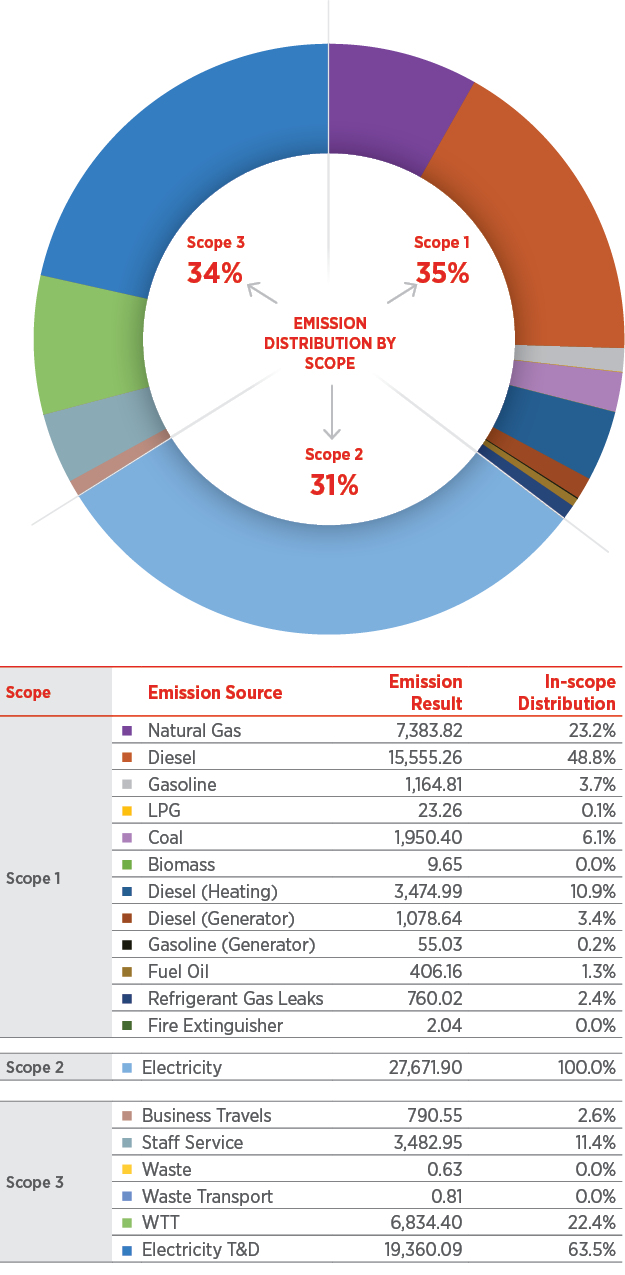
The graph on the next page shows the distribution of Scope 1 and Scope 2 greenhouse gas emissions by source. Emissions from electricity rank first with 47% (53.0% in 2021), while emissions from company vehicles rank second with 26% (19.5% in 2021), and emissions from natural gas consumption by 12% (6.9% in 2021). 9 - fuels used in buildings) is in the third place.
The theoretical payment amounts and the unit electricity price of the relevant year are taken into account in the calculation of emissions from electricity consumption in 2022.
Ziraat Bank 2022 Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Scope 1-2
Ziraat Bank also included business travels, personnel services, wastes, well-to-tank emissions and electricity transmission distribution categories, which are evaluated in Scope 3, in the 2022 carbon footprint calculations.
Ziraat Bank Distribution of Greenhouse Gas Emissions in 2022, Including Scope 3
Ziraat Bank met the 50,000 MWh consumption of its Head Office, subsidiaries and branches in 2022 from renewable energy sources, and took an important step towards reducing the carbon footprint caused by electricity consumption.
Ziraat Bank has documented its efforts in the field of sustainability and the transition to green transformation with the I-REC (The International REC Standard), the most widely used renewable energy certificate in the world. Thus, the Bank achieved a 19.6% reduction in its 2022 emissions (according to the 2022 I-REC-free result).
In 2022, Ziraat Bank’s emissions increased by 5.4% compared to 2021. Among the reasons for this increase are the decrease in the effects of the pandemic and the expansion of the calculation scope by detailing the emission sources in the emission calculations for 2022.
Ziraat Bank met the 50,000 MWh consumption of its Head Office, subsidiaries and branches in 2022 from renewable energy sources.
Change in Direct Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Direct GHG Emissions (Scope 1) |
2021 |
2022 |
% |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Direct Energy Consumption |
Direct GHG Emissions (tCO2e) |
Direct Energy Consumption |
Direct GHG Emissions (tCO2e) |
Scope 1 Change |
|
Natural Gas |
47,698 |
9,662 |
3,424,249.04 |
7,383.82 |
-24 |
Fuel Oil |
339 |
92 |
151,618.54 |
406.14 |
341 |
Diesel (for heating in buildings) |
1,710 |
381 |
1,272,924.53 |
3,474.99 |
812 |
Coal |
6,936 |
2,175 |
1,611,947,482 |
1,950.4 |
-10 |
Pellet |
301 |
4 |
87,901.31 |
9.65 |
141 |
Diesel |
52,072 |
14,105 |
5,629,916.07 |
15,555.26 |
10 |
Gasoline |
222 |
58 |
496,031.68 |
1,164.81 |
1,908 |
Leak Emissions |
0 |
7,771 |
395.37 |
762.06 |
-90 |
LPG |
- |
- |
7,785.04 |
23.26 |
- |
Generator Diesel |
- |
- |
395,117.00 |
1,078.64 |
- |
Generator Gasoline |
- |
- |
24,302.00 |
55.03 |
- |
As seen in the table below, Ziraat Bank’s energy indirect greenhouse gas emissions decreased by 28.24% compared to 2021. Although electricity consumption has increased by approximately 34%, one of the reasons for the decrease in emissions is the decrease in the electricity emission factor of the country in 2022, with the decrease in fossil fuel use in electricity generation in Turkey compared to the previous year.
For the emission factor used in the calculation of the current year’s emissions from electricity consumption, the previous year is taken into account when the data on the energy resources used in Turkey’s electricity production are available. The second reason is that 50,000 MWh of the electricity consumed in the Bank comes from renewable energy with I-REC. The emission factor of electricity from renewable energy is zero.
Ziraat Bank’s energy indirect greenhouse gas emissions decreased by 28.24% compared to 2021. Although electricity consumption has increased by approximately 34%, one of the reasons for the decrease in emissions is the decrease in the electricity emission factor of the country in 2022, with the decrease in fossil fuel use in electricity generation in Turkey compared to the previous year.
Ziraat Bank has documented its efforts in the field of sustainability and the transition to green transformation with the I-REC (The International REC Standard), the most widely used renewable energy certificate in the world.
Change in Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 2) |
2021 |
2022 |
% |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Indirect Energy Consumption |
Indirect GHG Emissions (tCO2e) |
Indirect Energy Consumption |
Indirect GHG Emissions (tCO2e) |
Scope 2 |
|
Electricity Purchased (kWh) |
84,403.363 |
38,564 |
112,890,687.28 |
27,671.90 |
-28.24 |
In the calculation of greenhouse gas emissions for the year 2022, Business Travels, Personnel Services, Wastes, Emissions from Well to Tank and Electricity Transmission Distribution emissions are taken into account within the Other Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions called Scope 3.

The greenhouse gas inventory for 2022 was realized as 90,005.4 tCO2e.
Other Indirect Greenhouse Gas Emissions (Scope 3)
Indirect Greenhouse Gas Sources |
(tCO2e) |
|---|---|
Business Travels |
790.55 |
Staff Service |
3,482.95 |
Waste |
0.63 |
Waste Transport |
0.81 |
WTT |
6,834.40 |
Electricity T&D |
19,360.09 |
In order to determine the difference compared to previous years, only Scope 1 and Scope 2 emissions have been included in the table below and a comparison has been made. In 2022, emissions increased by 5.4% compared to the previous year. In 2022, the intensity of greenhouse gas emissions according to Ziraat Bank’s net interest income is 0.000000741.
Ziraat Bank Greenhouse Gas Changes by Years
Greenhouse Gas Emissions |
Scope 1 (tCO2e) |
Scope 2 (tCO2e) |
Total tCO2e (Scope |
Change in total tCO2e % |
Greenhouse Gas Density (tCO2e/TL million revenue) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2022 |
31,864.08 |
27,671.9 |
59,535.9 |
-18.19 |
0,038 |
2021 |
34,335.9 |
38,564.1 |
72,900.0 |
1.35 |
0,053 |
2020 |
32,728.7 |
39,110.4 |
71,437.2 |
-11.89 |
0,076 |
2019 |
33,779.8 |
47,754.3 |
81,534.1 |
7.48 |
0,125 |
2018 |
29,015.4 |
46,841.5 |
75,856.9 |
-13.34 |
0,141 |
2017 |
33,428.6 |
54,234.3 |
87,662.9 |
3.14 |
0,202 |
2016 |
36,478.0 |
48,394.7 |
84,872.7 |
-5.27 |
0,237 |
2015 |
40,441.0 |
49,151.6 |
89,592.6 |
17.31 |
0,296 |
2014 |
36,060.5 |
40,311.2 |
76,371.6 |
- |
0,308 |
Ziraat Bank’s greenhouse gas inventory uncertainty for 2022 is calculated as 3.74% for Scope 1 and 2. Scope 3 uncertainty calculation is 5.74%. In the uncertainty calculations, the uncertainty rates of fuels are taken as high due to the payment amounts of the data and the consumption statements of the branches. For Scope 1-2, this value is considered “reasonable” below the 5% value specified in the GHG Protocol Standard. Scope 3 uncertainty, on the other hand, is at the “limited” level with a value of 5.74%. In the coming years, significant improvements are expected in the uncertainty ratio and analysis with data collection on consumption data.
SCOPE 1-2 ACCOUNT OF UNCERTAINTY |
||||||||||||
Greenhouse Gas Source |
Activity Data |
Unit |
Activity Data Uncertainty (%) |
EF |
Unit |
Emission Factor Uncertainty (%) |
tons, |
Calculated Emissions Uncertainty |
External Variable 1 |
External Variable 2 |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Steady Burning |
Natural Gas |
2,739.40 |
tons |
3.00 |
2.695 |
tons CO2eq/tons |
5.00 |
7,383.82 |
5.83 |
430.5470224 |
185,370.7385 |
|
Steady Burning |
Biomass |
87.90 |
tons |
7.00 |
0.110 |
tons CO2eq/tons |
5.00 |
9.65 |
8.60 |
0.829774975 |
0.688526509 |
|
Constant Combustion Generator |
Diesel |
395,117.00 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.003 |
tons CO2eq/L |
5.00 |
1,078.64 |
8.60 |
92.78819526 |
8,609.64918 |
|
Constant Combustion Generator |
Gasoline |
24,302.00 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.002 |
tons CO2eq/L |
5.00 |
55.03 |
8.60 |
4.733717794 |
22.40808415 |
|
Constant Combustion Coal |
Coal |
1,611.95 |
tons |
7.00 |
1.210 |
tons CO2eq/tons |
5.00 |
1,950.40 |
8.60 |
167.7793737 |
28,149.91824 |
|
Steady Combustion Kitchen Tube |
LPG |
7.79 |
tons |
7.00 |
2.987 |
tons CO2eq/tons |
5.00 |
23.26 |
8.60 |
2.000516557 |
4.002066494 |
|
Fixed Combustion Heating Diesel |
Diesel |
1,272,924.53 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.003 |
tons CO2eq/L |
5.00 |
3,474.99 |
8.60 |
298.930114 |
89,359.21304 |
|
Constant Combustion Fuel Oil |
Fuel Oil |
151,618.54 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.003 |
tons CO2eq/L |
5.00 |
406.16 |
8.60 |
34.93893908 |
1,220.729464 |
|
Moving Combustion On Road |
Diesel |
5,629,916.07 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.003 |
tons CO2eq/L |
5.00 |
15,555.26 |
8.60 |
1.338.114329 |
1,790,549.959 |
|
Moving Combustion On Road |
Gasoline |
496,031.68 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.002 |
tons CO2eq/L |
5.00 |
1,164.81 |
8.60 |
100.2010004 |
10,040.24049 |
|
Leak Emissions |
Gas Leaks |
395.37 |
kg |
7.00 |
1.922 |
tons CO2eq/kg |
5.00 |
760.02 |
8.60 |
65.37944106 |
4,274.471313 |
|
Leak Emissions |
Fire Extinguisher |
2,044.4 |
kg |
7.00 |
0.001 |
5,00 |
5.00 |
2.04 |
8.60 |
0.175865938 |
0.030928828 |
|
Purchased Electricity |
112,890,687.28 |
kWh |
3.50 |
0.000 |
tons CO2eq/kWh |
5.00 |
27, 671.90 |
6.10 |
1,688.893078 |
2,852,359.83 |
||
Total Emissions, tons CO2 eq |
59,535.98 |
|
|
Total Uncertainty |
3.74% |
SCOPE 3 ACCOUNT OF UNCERTAINTY |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Greenhouse Gas Source |
Activity Data |
Unit |
Activity Data Uncertainty (%) |
EF |
Unit |
|
Emission Factor Uncertainty (%) |
tons, CO2e |
Calculated Emissions Uncertainty |
External Variable 1 |
External Variable 2 |
Electric T&D |
112,890,687.28 |
kWh |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/kWh |
|
5.00 |
19,360.09 |
8.60 |
1,665.417686 |
2,773,616.07 |
Natural Gas |
2,739.40 |
tons |
7.00 |
0.43 |
tons CO2eq/tons |
|
5.00 |
1,190.07 |
8.60 |
102.3740579 |
10,480.44772 |
Heating Diesel |
1,272,924.53 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/L |
|
5.00 |
800.34 |
8.60 |
68.84772694 |
4,740.009505 |
Fuel Oil |
151,618.54 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/L |
|
5.00 |
105.71 |
8.60 |
9.093775649 |
82.69675555 |
Generator Diesel |
395,117.00 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/L |
|
5.00 |
248.43 |
8.60 |
21.37040075 |
456.6940281 |
Generator Gasoline |
24,302.00 |
tons |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/tons |
|
5.00 |
14.65 |
8.60 |
1.260238472 |
1.588201006 |
LPG |
7.79 |
tons |
7.00 |
0.35 |
|
|
5.00 |
2.70 |
8.60 |
0.232390207 |
0.054005208 |
Coal |
1,611.95 |
tons |
7.00 |
0.39 |
|
|
5.00 |
633.72 |
8.60 |
54.51478476 |
2,971.861758 |
On Road Diesel |
5,629,916.07 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.00 |
|
|
5.00 |
3,539.75 |
8.60 |
304.5011037 |
92,720.92215 |
On Road Gasoline |
496,031.68 |
liter |
7.00 |
0.00 |
|
|
5.00 |
299.02 |
8.60 |
25.72291196 |
661.6681995 |
Staff Service |
34,056,375.59 |
km |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/km |
|
5.00 |
3,482.95 |
8.60 |
299.6143035 |
89,768.73084 |
Business Travels |
4,844.769.25 |
km |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/km |
|
5.00 |
790.55 |
8.60 |
68.00525534 |
4,624.714754 |
Waste |
29,400.00 |
kg |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/kg |
|
5.00 |
0.63 |
8.60 |
0.053853209 |
0.002900168 |
Waste Transport |
1,539.00 |
km |
7.00 |
0.00 |
tons CO2eq/km |
|
5.00 |
0.81 |
8.60 |
0.069776214 |
0.00486872 |
Total Emissions, tons CO2 eq |
30,469.42 |
||
|
|||
Total Uncertainty |
|
|
5.67% |
Emission Factors
|
Unit |
CO2 |
CH4 |
N2O |
kg CO2e/unit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Diesel (mobile combustion) |
liter |
74.1 |
0.0039 |
0.0039 |
- |
Gasoline (mobile combustion) |
liter |
69.3 |
0.025 |
0.008 |
- |
Natural Gas |
m3 |
56.1 |
0.001 |
0.0001 |
- |
Fuel Oil |
kg |
77.4 |
0.003 |
0.0006 |
- |
Diesel |
liter |
74.1 |
0.003 |
0.0006 |
- |
Coal (Lignite) |
kg |
101 |
0.01 |
0.0015 |
- |
Pellet (Biomass) |
kg |
100 |
0.3 |
0.004 |
- |
LPG |
kg |
63.1 |
0.001 |
0.0001 |
- |
Diesel - Generator |
liter |
74.1 |
0.003 |
0.0006 |
- |
Gasoline - Generator |
liter |
69.3 |
0.003 |
0.0006 |
- |
Refrigerants - R134A |
kg |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.300 |
Refrigerants - R600 |
kg |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3 |
Refrigerants - R410A |
kg |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.924 |
Fire Extinguishers - CO₂ |
kg |
1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
- |
Electricity (2014 grid) |
kWh |
0.49306 |
0.00019 |
0.00121 |
0.494 |
Electricity (2015 grid) |
kWh |
0.55036 |
0.00021 |
0.00139 |
0.552 |
Electricity (2016 grid) |
kWh |
0.48985 |
0.00018 |
0.00131 |
0.491 |
Electricity (2017 grid) |
kWh |
0.51047 |
0.00018 |
0.00147 |
0.512 |
Electricity (2018 grid) |
kWh |
0.50501 |
0.00018 |
0.00142 |
0.507 |
Electricity (2019 grid) |
kWh |
0.51200 |
0.00018 |
0.00156 |
0.514 |
Electricity (2020 grid) |
kWh |
0.47523 |
0.00016 |
0.00157 |
0.477 |
Electricity (2021 grid) |
kWh |
0.45531 |
0.00015 |
0.00143 |
0.457 |
Electricity (2022 grid) |
kWh |
0.44 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
- |
Surveillance of environmental and social impacts in project financing
With the financing it provides, Ziraat Bank extends support to large infrastructure projects such as airports, highways, bridges and renewable energy projects, which generate added value for the country’s economy and play an important role in job creation.
In line with its Responsible Banking approach, the Bank also considers possible environmental and social impacts in the transactions it evaluates within the scope of project finance, and requests information and documents from investors that the projects meet environmental and social standards.
In loan agreements related to multilateral project finance transactions involving Ziraat Bank, the Bank aims to eliminate environmental and social risks and/or minimize their effects by evaluating each project on an individual basis. In this framework, the Bank ensures compliance with the environmental and social standards accepted by international financial institutions and recommended by project consultants.
In project finance contracts prepared by Ziraat Bank, the Bank receives statements and commitments from customers regarding environmental and social issues in accordance with the laws and regulations to which the customers are bound, as well as issuing notes of default in instances of failure to comply with the declarations and commitments. In this context, customer commitments are regularly monitored through periodic reports prepared by environmental consultants or investors.
Ziraat Bank controls its direct and indirect environmental and social impacts through its Environmental and Social Impact Management Policy, which was formed with the aim of integrating the universally accepted principles of sustainability into its business model.
Environmental and Social Risk Assessment Model
Ziraat Bank controls its direct and indirect environmental and social impacts through its Environmental and Social Impact Management Policy, which was formed with the aim of integrating the universally accepted principles of sustainability into its business model. With this policy, which determines the environmental and social impact management principles within the scope of its lending activities, the Bank prioritizes that the projects it finances include a high environmental and social contribution.
Ziraat Bank rejects financing the activities which are included in the “List of Unfunded Activities” annexed to its Environmental and Social Impact Management Policy and which are prohibited/restricted by national legislation and international agreements to which our country is a party, regardless of amount and without subjecting them any financial, technical, environmental and social impact evaluation.
The Bank subjects new/capacity-increasing investment projects and customers requesting loans, which are not in this list, to the Environmental and Social Risk Assessment Model established within the scope of the Environmental and Social Impact Management System.
Projects within the scope of Environmental and Social Risk Assessment Model are classified classified in 3 categories as high (A), medium (B) and low (C) risk.
Category A projects are potentially irreversible or have not been encountered before, with serious adverse social and environmental impacts. Category B projects are potentially few, only localized, largely irreversible projects with limited adverse environmental and social impacts for which measures have already been taken to mitigate their impact. Category C are projects with minimal or no social or environmental impact.
Actions and monitoring studies taken by Ziraat Bank for projects in high and medium risk categories:
- The investor must complete the project’s documentation (EIA Report, Project Description File, opinion letters, decisions, etc.) within the scope of the Environmental Impact Assessment Regulation (EIA) and must have obtained all environmental and social temporary permits.
- During the investment, the investor will ensure that environmental and social measures are successfully implemented, as specified and approved in the EIA Report or Project Introduction File, and will demonstrate with supporting documents that these practices are carried out regularly.
- An Environmental and Social Due Diligence/Action and Monitoring Plan will be prepared by an independent Environmental and Social Consultant/Expert in accordance with the Performance Standards of the International Finance Corporation (IFC) in order to monitor and regularly report all environmental and social aspects of the investment.
- The investment will be monitored by an independent Environmental and Social Consultant/Expert at least once a year with a site visit. After the investment is completed, the site will be visited once during the operation period and the investment will be monitored. A contract clause requiring the investor to comply with the Action and Monitoring Plans will be included in the loan agreement.
- Since there is no additional action to be taken to eliminate potential environmental-social risks in low-risk projects, monitoring is carried out within the framework of the Bank’s procedures and principles for monitoring investment loans.
- The annual application results and annual monitoring results of the environmental and social risk assessment are presented to the Corporate Governance Committee at the annual environmental and social management system evaluation meeting, within the scope of the Bank’s Sustainability Policy.
There were no projects rejected due to the Unfunded Activities (FEF) list in 2022, in which 21 projects were evaluated in terms of environmental and social aspects within the scope of Environmental and Social Impact Management Policy.
The distribution of the projects evaluated in 2022 within the scope of the Environmental and Social Impact Management Policyaccording to their categories is as follows:
Risk Category- # of projects
High risk (A) 7
Moderate Risk (B) 6
Low Risk (C) 8
Sectoral distribution of the evaluated projects (#)
Manufacturing 16
Energy 2
Tourism 3
For Environmental and Social Impact Management Policy and List of Unfunded Activities:
https://www.ziraatbank.com.tr/en/our-bank/sustainability/our-policies/environmental-and-social-impact-management-policy-in-lending-activities
Ziraat Bank continuously improves its environmental performance in order to inherit a cleaner and more livable world for future generations.
Efficient use of energy resources
Ziraat Bank continuously improves its environmental performance in order to leave a cleaner and more livable world to future generations. In this context, the Bank has implemented many innovative practices regarding energy saving and the efficient use of energy resources.
Ziraat Bank realized the installation of 352 air conditioning systems equipped with high-efficiency inverter technology using ozone-friendly R410A coolant gas in 2022.
A total of 62 of these air conditioning systems that were installed in order to reduce the cost of heating and increase energy efficiency were procured in accordance with the next generation VRF system standard which maximizes both energy savings and comfort. A total of 2.34 tons of R410A coolant gas was used in the installed systems.
Effective waste management activities
Empty toner and drum units which are not used in Ziraat Bank branches are disposed of under the supervision of the manufacturer. In 2022, a total of 10.620 kg of waste products were accredited and disposed of by the responsible recycling company.
Within the scope of the practices undertaken to reduce the use of toner in the Bank, the number of dots used for each character and the optimal number of points are adjusted and dots which cannot be discerned by the user are not printed, thus resulting in a 20% saving in toner use. The savings achieved prevented carbon dioxide emissions totaling 545.650 kg in 2022.
In addition, the Bank’s printer inventory is being replaced with new generation inkjet products which consume considerably less energy and minimize the harm to the environment in terms of waste.
Defective IT equipment in the Ziraat Bank units and branches is collected in Bank service centers and returned to use by carrying out repairs and renewals.
Waste IT materials, sheet metal materials such as system cabinets and air conditioning units, battery and scrap ATM devices are sold on to companies which hold transportation and processing licenses issued by the Ministry of Environment and Urbanization. Thus, waste is treated as a raw material through recycling, preventing such waste from harming the environment. In this framework, approximately 73 tons of waste material was sent to recycling in 2022.
Creating added value by saving paper
Ziraat Bank creates added value with its activities carried out within the framework of the banking principle that respects people and the environment, in line with its Sustainability Policy.
Sustainable Banking Process Audit was included in the audit plan in 2022 in order to evaluate Ziraat Bank’s efforts within the framework of the concept of sustainability, which is one of the main agenda items of both governments and institutions in recent years.
In this context; In line with syndicated loan requirements, sustainability performance criteria (Key Performance Indicator (KPI)), environmental loan products included in the concept of sustainability, the Bank’s general compliance level with the strategies and policies of national and international authorities in the field of sustainable banking were examined.
Within the scope of the audit model that Ziraat Bank implements, the practice of submitting physical documents and reports was discontinued, with branch reports instead being generated through the system. In addition to branch audits, audit reports for all head office units have been prepared and monitored through the system.
In addition, with the e-signature and virtual archive application in use throughout the Bank, all audit and review/investigation reports are archived digitally on the main banking software without the need for a physical document archive.
The transfer of audit and inspection and investigation reports to the system and the virtual archive application saved the need for 32,000 sheets of A4 paper. A4 paper consumption throughout the Bank stood at 248,000 packages in 2022.
The transfer of audit and inspection and investigation reports to the system and the virtual archive application saved the need for 32,000 sheets of A4 paper.
Ziraat Bank creates added value with its activities carried out within the framework of the banking principle that respects people and the environment, in line with its Sustainability Policy.
Other environmental practices
Ziraat Bank aims to obtain LEED Certification by designing the Ziraat Towers to be built at the Istanbul International Finance Center campus, which is based in Ataşehir, İstanbul, in accordance with international environmental standards.
In the course of the continuous improvement work undertaken in physical service points, the materials used in construction projects such as installations, electrical components, equipment, furniture and furnishings are examined by Ziraat Bank within the scope of R&D work, and the functionality and recycling properties of the materials are taken into consideration with concepts which will minimize damage during the selection, with consideration given to the environmental impact. In line with the sustainability concept, 100 service buildings were renovated at the Bank in 2022.




